Guide for embedding via wireframe
Last Updated: August 16, 2025
1. Overview of the flow
Embedding ResourcePlanner uses a short‑lived JWT (JSON Web Token) to grant access to a particular workspace for a specific user. The token is generated by your backend using an API key unique to your workspace. The high‑level steps are:
- Your backend calls ResourcePlanner: Your backend sends a request to
https://resourceplanner.io/api/embed-url, including the workspace API key in the headers and the user's email in the request body. - ResourcePlanner returns a signed embed URL: The response contains a URL like
https://resourceplanner.io/sso/<token>. This URL encodes a short‑lived JWT ResourcePlanner's side. - Backend returns embed URL to frontend: Your backend returns the full URL to your frontend.
- Frontend embeds the page: The front‑end uses an
<iframe>with the returned URL as thesrcattribute.
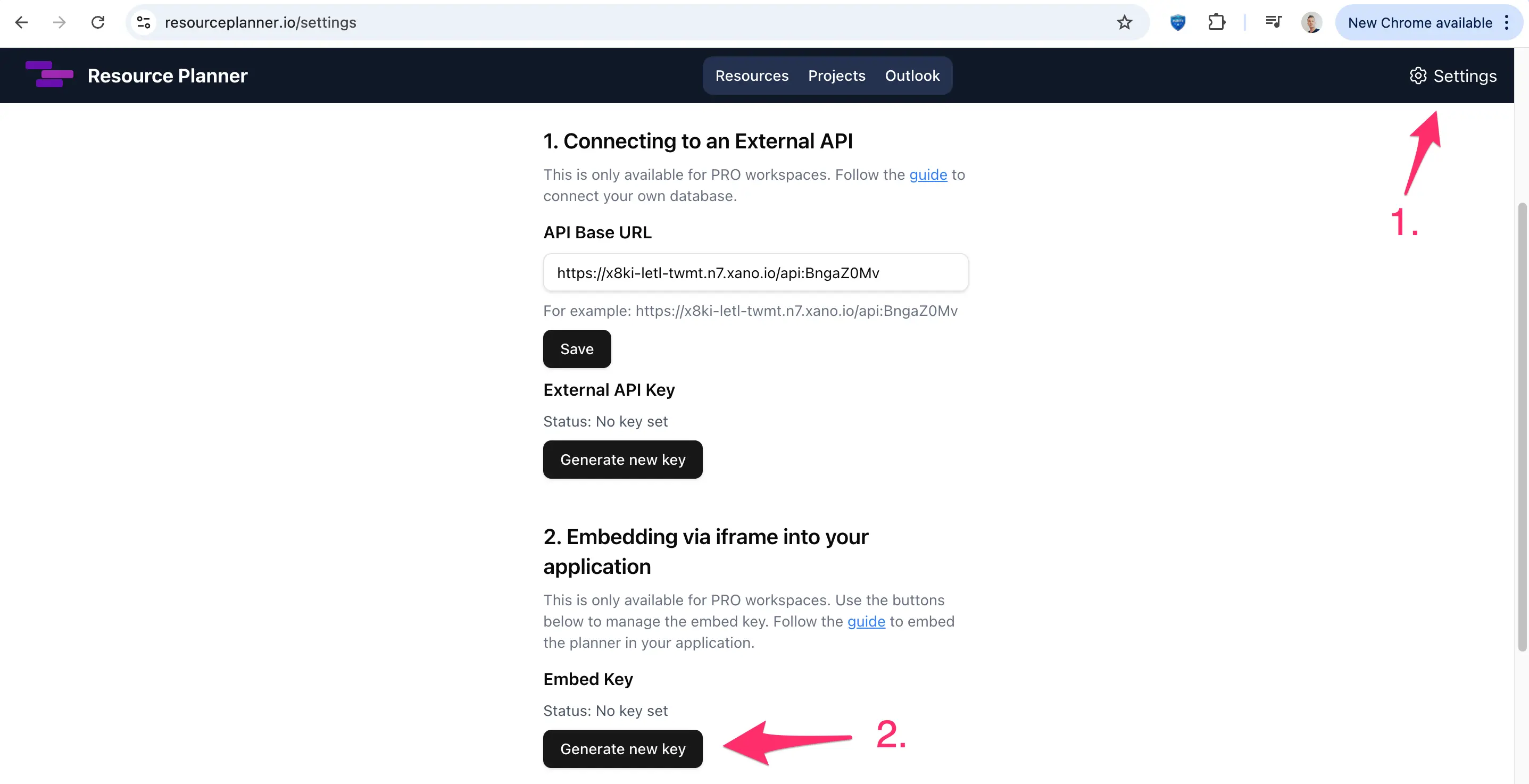
2. Preparing your workspace
- Generate a workspace API key: Each ResourcePlanner workspace has a unique secret. Treat this key like any API secret: store it in your backend or secrets manager and never expose it in the browser or frontend.
- Register users: Ensure that every email that will request an embed corresponds to a user in ResourcePlanner and that the user belongs to the workspace. The embed API will refuse to generate a token for emails that are not linked to the workspace.
3. Implementing the backend endpoint
Your backend will act as a proxy between the frontend and ResourcePlanner. Below is an example in Node.js; similar logic applies to Xano or other platforms.
// Example pseudo-code for a Node/Express backend
import fetch from 'node-fetch';
app.post('/get-resourceplanner-embed', async (req, res) => {
const response = await fetch('https://resourceplanner.io/api/embed-url', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'x-api-key': process.env.WORKSPACE_API_KEY,
},
body: JSON.stringify({ email: youremail@yourdomain.com }),
});
if (!response.ok) {
const error = await response.json();
return res.status(response.status).json(error);
}
const { embed_url } = await response.json();
return res.json({ embed_url });
});Key points
- Never expose
API keyon the client. All calls to ResourcePlanner's API must originate from your backend. Exposing secrets in the browser would allow anyone to generate tokens for your workspace.
4. Embedding in frontend
On the frontend, you will call your backend endpoint and create an iframe with the returned URL. The following steps outline a typical approach:
Create a custom action (e.g., getResourcePlannerEmbed). Inside this action:
async function getResourcePlannerEmbed(email) {
const res = await fetch('https://your-backend.com/get-resourceplanner-embed', {
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify({ email }),
});
if (!res.ok) throw new Error((await res.json()).error || 'Failed to get embed URL');
const { embed_url } = await res.json();
return embed_url;
}Use the returned URL in an iframe. You can bind the src of an iframe component to the value returned by the action. Alternatively, you can dynamically add an iframe element via JavaScript:
const url = await getResourcePlannerEmbed(currentUser.email);
const iframe = document.createElement('iframe');
iframe.src = url;
iframe.width = '100%';
iframe.height = '600';
iframe.style.border = 'none';
document.getElementById('resourceplanner-container').appendChild(iframe);Prevent token leakage. Because the token is part of the URL, set a strict referrer policy so the full URL isn't sent to third‑party domains if users click links. Add a meta tag to your frontend project head:
<meta name="referrer" content="no-referrer" />This instructs browsers not to include the URL in the Referer header.
If you run into any issues, please contact me at adam@resourceplanner.io