Developer Integration Guide – Resource Planning API
Last Updated: October 18, 2025
1. Overview of the Data Model
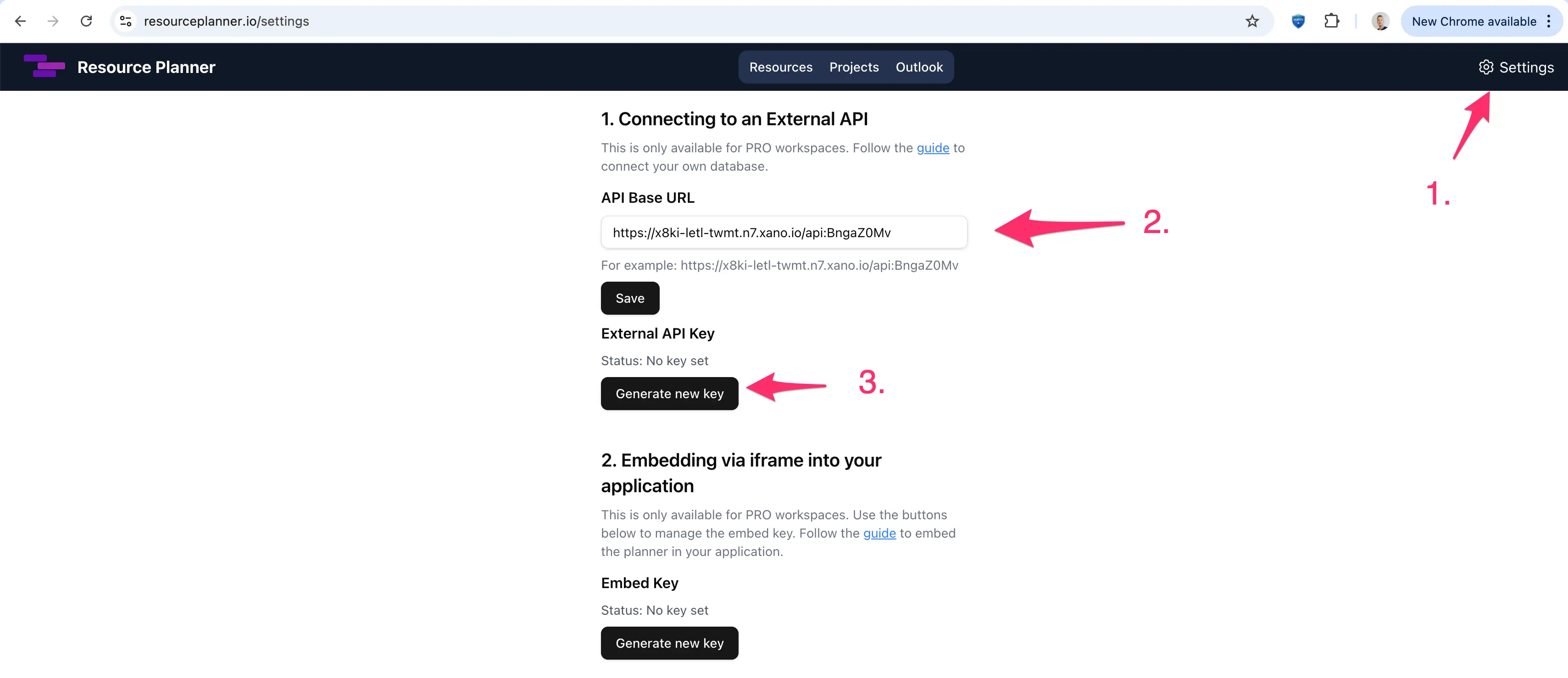
This document explains how third‑party developers can integrate an external data source with the application. You configure your own API base URL, and the app's server proxies requests to your API.
The application works with three core entities:
- Resources – people or assets that can be assigned to projects. Minimum fields:
id,name,email,capacity(decimal), andwork_days(array of integers 1–7). - Projects – initiatives resources can be scheduled against. Supported fields:
id,title, optionalnote,color(any hex color, but we recommend avoiding gray, red and green as these are colors we use for statuses). - Assignments – link a resource to a project with a date range and a daily allocation. Fields:
id,project_id,resource_id,date_from,date_to,hours_per_day, optionalnote.
2. API Endpoints
The server proxies requests to your configured apiBaseUrl. Endpoints should be relative to your API root and return JSON. You should have the following endpoints, so the app works correctly:
2.1 /loadData
On GET, return all resources, projects, assignments, plus any embedded memberships in a single payload.
{
"resources": [
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Alice",
"email": "alice@example.com", // optional
"capacity": 37.5,
"work_days": [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
}
],
"projects": [
{
"id": 42,
"title": "Migration Project",
"note": "Phase 1 rollout", // optional
"color": '#D71DF4', // optional
"enum_status_id": 1
}
],
"assignments": [
{
"id": 7,
"project_id": 42,
"resource_id": 1,
"date_from": "2025-09-01",
"date_to": "2025-09-10",
"hours_per_day": 8,
"note": "Polishing UI", // optional
}
]
}2.2 /resources
| Method | Endpoint | Description |
|---|---|---|
| POST | /resources | Create a resource; return the created record with embedded membership. Pass invited=true when you want the app to email an invitation; omit the membership block entirely to add a resource without inviting them yet. Supply access details inside the nested membership object:The response includes the persisted membership snapshot: Membership field reference
You can omit the |
| PUT | /resources/{id} | Update a resource; supply the changed fields only. Provide the membership object when adjusting roles, visibility, or customer permissions. |
| DELETE | /resources/{id} | Delete a resource and its assignments; return status 200. We try to delete all assignments of this resource on external API, but we don't block the operation if it fails. |
2.3 /projects
| Method | Endpoint | Description |
|---|---|---|
| POST | /projects | Create a project; return the created record. For example: |
| PUT | /projects/{id} | Update a project; return the updated record. For example: |
| DELETE | /projects/{id} | Delete a project (and its assignments); return status 200. We try to delete all assignments of this project on external API, but we don't block the operation if it fails. |
2.4 /assignments
| Method | Endpoint | Description |
|---|---|---|
| POST | /assignments | Create an assignment; return the created record. For example: |
| PUT | /assignments/{id} | Update an assignment; return the updated record. For example: |
| DELETE | /assignments/{id} | Delete an assignment; return status 200. |
3. Authentication & Workspace selection
Protect your API with authentication. The planner's server signs outbound requests with Authorization: Bearer <KEY>.
Since requests originate from our server to yours, typical browser CORS restrictions do not apply. Ensure your API allows requests from our deployment environment (standard server‑to‑server access).
4. Normalisation and Data Conversion
- Dates: Provide ISO 8601 strings (
YYYY-MM-DD). The client parses them to Dates. - Numbers:
hours_per_dayis converted to a float. Prefer dot as decimal separator. - IDs: Numeric IDs are accepted and coerced to strings internally.
- Work days:
work_daysis an array of integers 1–7 (Mon–Sun).
5. Sending Requests
Every outbound call from Resource Planner to your API contains the workspace API key in the Authorization header. When testing directly, use the same key:
curl -X POST https://yourapp.com/api/resources \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API_ACCESS_KEY>" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"name": "Charlie Manager",
"email": "charlie@example.com",
"membership": {
"role": "manager",
"memberSettings": { "visibility": "team" },
"managerSettings": {
"scope": "managed",
"managesResources": ["RESOURCE_ID"],
"canSeeFinancials": true
}
}
}'The body above uses the nested membership object; the backend normalises it to the canonical membership shape before persisting.
6. Example Workflow
- Initial data load – Client calls
GET /loadDataand normalises the response. - Creating a project –
POST /projects; - Creating a resource –
POST /resources; - Assigning a resource –
POST /assignments; with respectiveresource_idand project_id. - Updating or deleting –
PUT/DELETEthe relevant entity. We do optimistic updates on client, but we show error messages on failure, so user can reload the page.